Know Your Heart
The heart, at the core of the cardiovascular system, pumps oxygen-rich blood through a vast network of vessels, delivering essential nutrients while removing waste.
Understanding how your heart works empowers you to make informed choices, reduce risks, and recognise early warning signs of heart conditions.
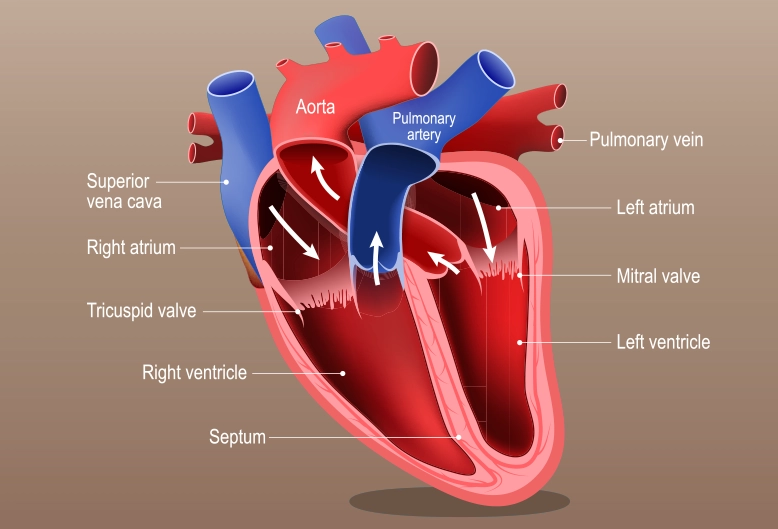
Right Side of the Heart (Deoxygenated Blood Circulation)
- Superior Vena Cava
A major vein that collects deoxygenated blood from the upper body and delivers it to the right atrium.
- Right Atrium
The entry point for deoxygenated blood, which it receives from the superior and inferior vena cava before pumping it into the right ventricle.
- Tricuspid Valve
Controls the one-way blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle, ensuring efficient circulation.
- Right Ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, playing a crucial role in oxygen exchange.
- Pulmonary Valve
Directs blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, ensuring smooth circulation.
- Pulmonary Artery
Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation.
Left Side of the Heart (Oxygenated Blood Circulation)
- Pulmonary Vein
Responsible for returning oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium, ensuring a constant oxygen supply.
- Left Atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins before passing it to the left ventricle.
- Mitral Valve
Regulates blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle, preventing backflow.
- Left Ventricle
The strongest and most muscular chamber, responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to the body.
- Aorta
The largest artery in the body, carrying oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to all organs and tissues.
Common Heart Conditions -
Understanding Cardiovascular Diseases
Ischaemic heart disease, including coronary artery disease (CAD), is a leading cause of death, often due to narrowed or blocked arteries reducing blood flow to the heart. Early detection and treatment are key to lowering risks and improving outcomes.
At Sunway Medical Centre Velocity, our heart specialists use advanced technology to diagnose, treat, and manage a range of cardiovascular conditions, from heart rhythm disorders to congenital defects. Timely medical attention and personalised care are essential for maintaining heart health and preventing complications.
Arrhythmia (Heart Rhythm Disorder)

Arrhythmia is a condition where the heart beats irregularly, too fast (tachycardia), or too slow (bradycardia). This occurs due to disruptions in the heart’s electrical system. While some arrhythmias are mild, others can lead to life-threatening complications like stroke or sudden cardiac arrest. Symptoms may include heart palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, and fainting. Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications and medications to procedures like electrical cardioversion, pacemakers, or catheter ablation.
Read More
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This restricts oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart, increasing the risk of chest pain (angina), heart attack, or heart failure. CAD is often caused by high cholesterol, smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, or an unhealthy lifestyle. Early detection and lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, can help manage the condition and reduce complications.
Read More
Heart failure happens when the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body. This condition can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, swelling in the legs, and persistent fatigue. Heart failure can be caused by underlying conditions such as CAD, hypertension, or heart valve disorders. While it is a chronic condition, lifestyle changes, medications, and medical treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Read More
Valvular heart disease affects one or more of the heart’s four valves—mitral, aortic, tricuspid, and pulmonary—causing them to narrow (stenosis), leak (regurgitation), or not close properly (prolapse). These issues disrupt normal blood flow, forcing the heart to work harder. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, dizziness, and fatigue. Treatment options range from medication to surgical valve repair or replacement, depending on the severity of the disease.
Read More
Congenital Heart Conditions

Congenital heart conditions refer to structural heart defects present at birth, ranging from minor abnormalities to life-threatening defects. Some require surgery, medication, or long-term monitoring, while others may have little impact on daily life.
Read More
Myocardium Disease (Cardiomyopathy)

Myocardium disease, or cardiomyopathy, is a condition where the heart muscle becomes thickened, stiff, or weakened, affecting its ability to pump blood efficiently. It can be genetic or develop due to high blood pressure, heart attacks, infections, or other diseases. Symptoms may include fatigue, swelling, irregular heartbeats, and breathlessness. Treatment options focus on managing symptoms, slowing progression, and reducing complications through medication, lifestyle changes, or implantable devices.
Read More
Pericardium Disease (Pericarditis)
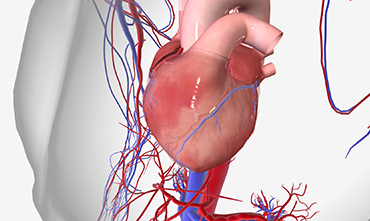
Pericardium disease involves inflammation or fluid accumulation around the heart’s protective sac, known as the pericardium. This condition can result from infections, autoimmune diseases, heart attacks, or kidney failure. Symptoms often include sharp chest pain that worsens with deep breathing, fever, and fatigue. In most cases, pericarditis resolves with medication, but severe cases may require drainage procedures or surgery to relieve pressure on the heart.
Read More
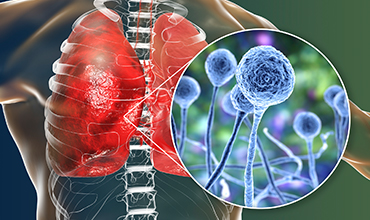
Thoracic disease refers to conditions that affect the organs and structures within the chest, including the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. It can encompass a range of issues, such as thoracic aortic aneurysms, lung diseases, and mediastinal tumours. Depending on the specific condition, symptoms may include chest pain, breathing difficulties, and circulation problems. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention are essential to managing thoracic diseases effectively.



























